If I Cancel During Middle of Backing Up Then When I Back Up Again Do Data Gets Duplicated
Cloud backup, also known as online fill-in or remote backup, is a strategy for sending a copy of a concrete or virtual file or database to a secondary, off-site location for preservation in instance of equipment failure or catastrophe. The secondary server and data storage systems are usually hosted by a third-political party service provider, who charges the backup customer a fee based on storage space or chapters used, data transmission bandwidth, number of users, number of servers or number of times data is accessed.
Implementing cloud data backup can assistance eternalize an organization'southward data protection strategy without increasing the workload of information applied science (IT) staff. The labor-saving benefit may be significant and enough of a consideration to get-go some of the additional costs associated with cloud fill-in, such as data transmission charges.
About cloud subscriptions run on a monthly or yearly ground. While initially used mainly by consumers and domicile offices, online backup services are now commonly used by small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) as well as larger enterprises to back up some forms of data. For larger companies, cloud data backup may serve as a supplementary class of backup.
What is the deject?
Cloud computing is a general term that refers to hosted services that are delivered over the cyberspace. Different from traditional web hosting, the services on the deject are sold on demand, are offered in an elastic manner -- significant the customer tin use as much or equally lilliputian of the service equally needed -- and are managed completely past the service provider. Additionally, a cloud can be individual or public. A public cloud sells services to anyone on the internet, such as how Amazon Web Services (AWS) operates, while a private cloud supplies hosted services to a express number of users.
How cloud backup works
In an organization's data center, a backup awarding copies data and stores it on different media or another storage system for easy admission in the event of a recovery situation. While at that place are multiple options and approaches to off-site backup, cloud backup serves as the off-site facility for many organizations. In an enterprise, the visitor might own the off-site server if it hosts its own deject service, simply the chargeback method would be similar if the company uses a service provider to manage the cloud backup environment.
There are a variety of approaches to deject fill-in, with available services that can easily fit into an organization's existing data protection process. Varieties of cloud fill-in include:
- Backing up directly to the public cloud. Ane way to store organizational workloads is past duplicating resources in the public cloud. This method entails writing data directly to cloud providers, such every bit AWS or Microsoft Azure. The organization uses its own fill-in software to create the data re-create to send to the deject storage service. The cloud storage service then provides the destination and safekeeping for the information, but it does not specifically provide a backup application. In this scenario, information technology is important that the backup software is capable of interfacing with the cloud'southward storage service. Additionally, with public cloud options, It professionals may need to expect into supplemental data protection procedures.
- Backing up to a service provider. In this scenario, an organisation writes data to a cloud service provider that offers backup services in a managed information center. The backup software that the company uses to transport its data to the service may be provided equally function of the service, or the service may support specific commercially-available fill-in applications.
- Choosing a deject-to-cloud (C2C) backup. These services are among the newest offerings in the deject fill-in arena. They specialize in backing up data that already lives in the cloud, either as information created using a software as a service (SaaS) application or equally information stored in a cloud backup service. Equally its proper name suggests, a cloud-to-cloud backup service copies information from one cloud to some other cloud. The cloud-to-cloud backup service typically hosts the software that handles this process.
- Using online deject backup systems. There are likewise hardware alternatives that facilitate backing upwards data to a cloud backup service. These appliances are all-in-one backup machines that include backup software and disk chapters along with the fill-in server. The appliances are near as close to plug-and-play as backup gets, and most of them also provide a seamless (or most and so) link to one or more cloud backup services or cloud providers. The list of vendors that offer backup appliances that include cloud interfaces is long, with Quantum, Unitrends, Arcserve, Rubrik, Cohesity, Dell EMC, StorageCraft and Asigra active in this arena. These appliances typically retain the most recent backup locally, in addition to shipping it to the cloud backup provider, so that any required recoveries can exist made from the local backup copy, saving time and manual costs.
When an organization engages a cloud backup service, the first step is to complete a full backup of the data that needs to be protected. This initial backup can sometimes have days to finish uploading over a network as a result of the big book of data that is being transferred. In a 3-two-one backup strategy, where an organization has iii copies of data on two dissimilar media, at least one re-create of the backed upwardly data should be sent to an off-site backup facility and so that it is attainable even if on-site systems are unavailable.
Using a technique chosen cloud seeding, a cloud backup vendor sends a storage device -- such as a hard bulldoze or tape cartridge -- to its new client, which then backs up the data locally onto the device and returns it to the provider. This procedure removes the need to send the initial information over the network to the backup provider.
If the amount of data in the initial fill-in is substantial, the cloud backup service may provide a full storage assortment for the seeding process. These arrays are typically modest network-attached storage (NAS) devices that tin be shipped back and forth relatively easily. Subsequently the initial seeding, but inverse data is backed up over the network.
How data is restored
Cloud backup services are typically built around a client software awarding that runs on a schedule determined by the purchased level of service and the customer'south requirements. For case, if the customer has contracted for daily backups, the awarding collects, compresses, encrypts and transfers data to the cloud service provider's servers every 24 hours. To reduce the amount of bandwidth consumed and the time it takes to transfer files, the service provider might only provide incremental backups after the initial total backup.
Deject backup services oft include the software and hardware necessary to protect an organisation's data, including applications for Substitution and SQL Server. Whether a customer uses its own backup awarding or the software the cloud backup service provides, the organization uses that same awarding to restore backed up data. Restorations could be on a file-by-file basis, by volume or a full restoration of the complete backup.
Brien Posey discusses how deject backup recovery works and where information technology works best.
If the volume of data to be restored is very large, the deject fill-in service may transport the data on a complete storage array that the customer can claw upwards to its servers to recover its information. This is, in outcome, a opposite seeding process. Restoring a large amount of information over a network can have a long time.
A key feature of deject backup restorations is that they can be done anywhere from almost whatever kind of computer. For instance, an organization could recover its data straight to a disaster recovery site in a different location if its data center is unavailable.
Types of fill-in
In addition to the various approaches to cloud backup, in that location are also multiple fill-in methods to consider. While cloud fill-in providers give customers the option to cull the backup method that best fits their needs and applications, it is important to understand the differences amid the iii main types.
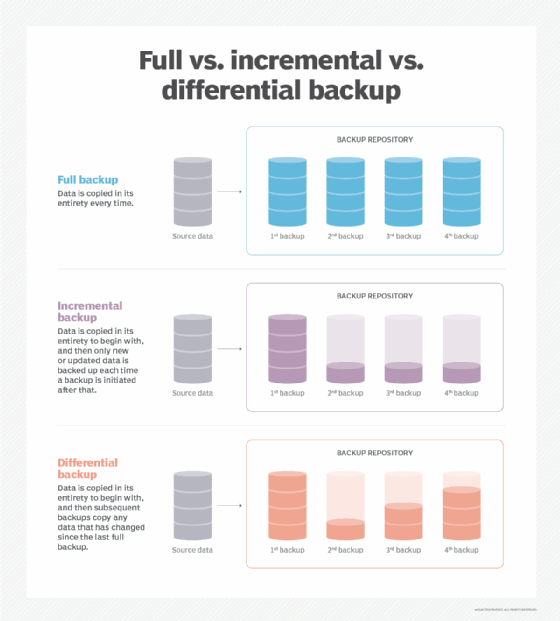
- Full backups copy the unabridged information gear up every time a backup is initiated. As a effect, they provide the highest level of protection. However, virtually organizations cannot perform total backups oft because they can be time-consuming and take up as well much data storage capacity.
- Incremental backups only back up the data that has been changed or updated since the terminal backup. This method saves time and storage space, but tin can brand it more difficult to perform a complete restore. Incremental is a common course of deject backup because it tends to utilise fewer resource.
- Differential backups are similar to incremental backups because they simply contain data that has been altered. However, differential backups back up data that has inverse since the last total backup, rather than the last backup in general. This method solves the problem of difficult restores that tin arise with incremental backups.
Pros and cons
Before choosing cloud backup as a backup strategy, it is of import to weigh the potential pros and cons that are associated with using a third-party to store data. The advantages of deject fill-in include:
- Generally, it is cheaper to support data using a cloud backup service compared to edifice and maintaining an in-house backup performance. The associated cloud fill-in costs will ascension equally the book of fill-in information rises, but the economies are likely to keep to make cloud backup an attractive selection. Some providers may offer complimentary cloud backup, only the amount of backup capacity typically has a storage limit, which makes gratis fill-in advisable for some dwelling house users and but the smallest of companies.
- The cloud is scalable, and so even as a company'south data grows, it tin even so be hands backed up to a cloud backup service. But organizations demand to be wary of escalating costs every bit data volume grows. Past weeding out dormant information and sending it to an annal, a company tin better manage the amount of information information technology backs up to the deject.
- Managing cloud backups is simpler considering service providers take care of many of the management tasks that are required with other forms of fill-in.
- Backups are more often than not more than secure against ransomware attacks because they are performed exterior of the office network. Fill-in data is typically encrypted before it is transmitted from the customer's site to the deject backup service, and usually remains encrypted on the service'south storage systems.
- Deject backups help lower the chance of mutual data backup failures acquired by improper storage, physical media damage or accidental overwrites.
- A cloud backup service can help to consolidate a company's fill-in data because the service tin can support master data center storage systems, remote office servers and storage devices, and end-user devices such as laptops and tablets.
- Backed up data is accessible from anywhere.
Despite its many benefits, there are some disadvantages and challenges to using a cloud backup service, including:
- The backup speed depends on bandwidth and latency. For instance, when many organizations are using the internet connectedness, the backup could be slower. This could be bothersome when bankroll data up, but could be an even greater issue when it is necessary to recover data from the service.
- Costs tin escalate when bankroll up big amounts of data to the cloud.
- As with any use of cloud storage, data is moved exterior of an organization'south buildings and equipment and into the control of an outside provider. Therefore, it is incumbent to learn every bit much as possible about the deject fill-in provider's equipment, physical security procedures, data protection process and fiscal viability.
All-time practices
While strategies, technologies and providers widely vary, there are several agreed upon best practices when it comes to implementing deject backup in the enterprise. In general, a few guidelines are:
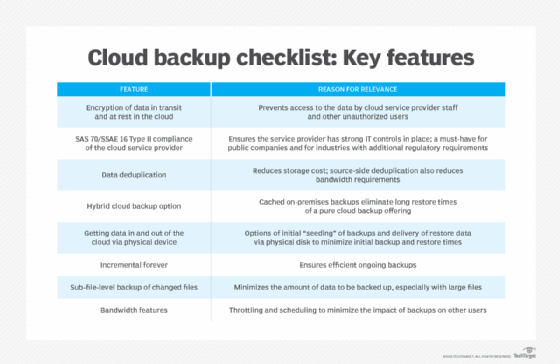
- Understand all aspects of the cloud fill-in provider service-level understanding (SLA), such equally how data is backed upwardly and protected, where vendor offices are located and how costs accrue over time.
- Practice not rely on any one method or information storage medium for fill-in.
- Exam backup strategies and information recovery checklists to ensure they are sufficient in the case of a disaster.
- Accept administrators routinely monitor cloud backups to brand sure processes are successful and uncorrupted.
- Choose a information restore destination that is hands accessible and does not overwrite existing data.
- Make decisions about specific data or files to back up based on the criticality of the information to business operations.
- Utilize metadata properly to enable the quick location and restoration of specific files.
- Consider using private encryption for data that must stay confidential.
Special considerations
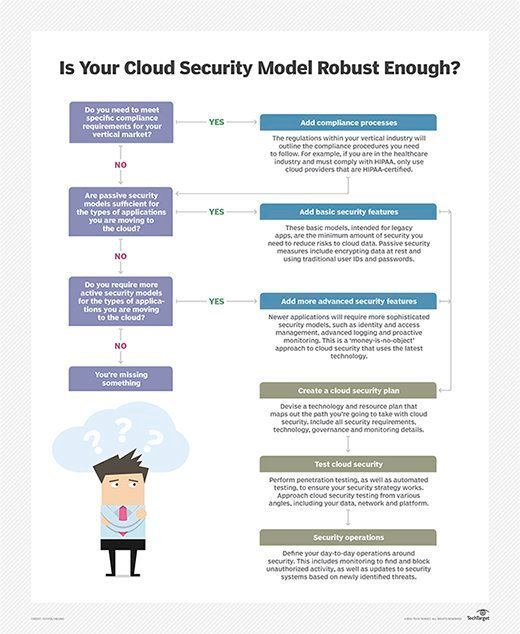
When choosing a cloud fill-in service provider, in that location are a few additional considerations to weigh. Some companies have special needs related to data protection, only not all cloud backup providers are able to come across those needs. For example, if a company must comply with a specific regulation such every bit HIPAA or GDPR, the cloud backup service needs to be certified as compliant with data handling procedures as defined by that regulation. While an outside firm provides the backup, the customer is still responsible for the data, and could face serious consequences -- including steep fines -- if the cloud backup provider does not maintain the data appropriately.
Data archiving is some other special consideration when selecting a deject backup service. Archiving is different from routine data backup. Archived data is data that is not currently needed merely still needs to be retained. Ideally, that information should be removed from the daily fill-in stream considering it is probable unchanged and information technology unnecessarily increases the volume of backup data transmissions. Some cloud backup providers offer archiving services to complement their backup products. Archive information is generally stored on equipment geared to longer retentions and infrequent access, such every bit record or low-performing disk systems. That type of storage is generally less expensive than information storage used for active backups.
Deject backup vs. cloud DR
Cloud fill-in and cloud disaster recovery are non the same, but they are continued. While cloud backup services can be tapped to recover data and resume operations after a confusing result, information technology should exist noted that they are non necessarily specifically oriented to provide all the avant-garde features and services that a true DRaaS offer would provide.
For instance, to apply the data that was saved to a deject backup service to recover from a disaster, information technology would have to include much more than just data files, such as operating systems, application software, drivers and utilities. Users would have to set up their fill-in routines to include those elements specifically, such as by mirroring entire servers to the cloud backup service.
George Crump, founder of analyst business firm Storage Switzerland, discusses the benefits of cloud disaster recovery.
More chiefly, a true DRaaS not only has the data and arrangement and application software fix to exist accessed, it as well provides the necessary servers -- physical or virtual -- and storage resources to spin up the clients' servers and applications so that they continue to operate and comport on with their business organization.
An organization must consider if the disaster recovery provider has enough bandwidth and resources to handle the data transfer, and thus how long it will take to perform a recovery. Testing is important and often easier than with traditional disaster recovery, considering many providers offer automated tests.
A deject backup provider may also offer disaster recovery in the cloud. Cloud disaster recovery is especially attractive for smaller businesses that do not take the funding or resources to support their own DR site. The cloud information center should be far plenty abroad from the organization using it to ensure recovery from any disaster.
Cloud vs. local fill-in
When looking into information backup options, ii chief product categories are deject backup and local backup. Local backup, also known as traditional backup, is the procedure of storing a copy of data on-site at the organization. In this arroyo, backup software is used to manage and copy the information to hardware such as tapes, disks or network-fastened storage devices.
In the enterprise, cloud information backup services were initially used for noncritical data. Traditional backup was considered ameliorate for disquisitional data that requires a short recovery fourth dimension objective (RTO) because there are physical limits as to how much information tin can be moved in a given amount of time over a network. When a big corporeality of information needs to be recovered, it may need to be shipped on tape or some other portable storage media. However, with most cloud backup schemes -- whether controlled by a user's backup software, the deject backup service app or a backup apparatus -- the most recently backed up data is retained on site likewise equally spun off to the cloud service. This organization provides all the benefits of cloud backup while leaving a local copy of the data that tin can exist used for quick recoveries.
Tape backup requires data to exist copied from a primary storage device to a tape cartridge. Cartridges take grown dramatically in chapters in recent years. LTO-8 tapes, released in tardily 2019, can store 12 TB of uncompressed data and 30 TB compressed. Record is a stiff storage medium in an age of exponential data growth. In addition to their capacity benefits, tapes are comparatively inexpensive to own and operate. Nonetheless, the restore process tin exist slow considering access is sequential.
While the deject appears to offer unlimited storage capacity, costs rise dramatically depending on how much an organization needs. Although admission is not sequential like with tape, restore times yet depend on the internet or individual communications lines, and crave an appropriate amount of bandwidth. Cloud service providers take some of the backup management work out of the process for organizations. The process of backing up to tape and maintaining the cartridges is essentially upwardly to the organization. There is more flexibility in the procedure of restoring from cloud backup because an organization tin restore to several different devices, including laptops and phones.
Deject and tape both provide protection from cyberattacks, such as ransomware. Deject backups are useful in the event of an attack because they are off-site. Tape backups are even more secure because they are offline.
Disk, while not as portable as tape, is another common medium for backup. The biggest do good to a disk is access speed. Disks offer random access and frequently meridian cloud and tape for restore speed. Disk-based backups are typically performed continuously throughout the mean solar day, while tape backs upward less regularly. A disk-based fill-in is self-contained, with less personnel interaction than with record, making the risk of human error smaller. Deejay-based backups can exist expensive, often costlier than tape or deject. The life bridge of disk is shorter than tape, and its immovability is weaker than that of tape. As long as the service provider is still in business, the life span of a cloud backup could be longer than that of deejay or record.
NAS fill-in uses a blazon of appliance that connects to a network, rather than a desktop or server, to accomplish a local backup. These appliances allow multiple devices and users on the aforementioned network to store, access and share data wirelessly. Both NAS and deject backup offer stiff data protection, high security and efficient recovery times, but since NAS appliances are located on the same local surface area network (LAN) as the devices being backed up, NAS backups are quicker to perform than cloud backups. However, deject backups tin can provide a lower initial price and a higher reliability in the instance of on-site disasters.
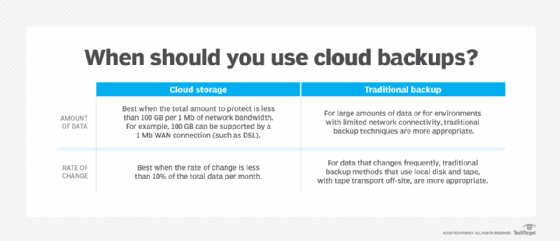
The post-obit chart helps to illustrate when deject information backups should be considered as a viable option.
With a proper retention policy, cloud backups can reduce or fifty-fifty replace the need for off-site tape data storage, so organizations are making the switch from disk-to-disk-to-tape (D2D2T) strategies to disk-to-disk-to-cloud (D2D2C).
Flexibility is some other benefit of the cloud because no additional hardware is needed.
File sync and share
There is ofttimes confusion amid the definitions of cloud fill-in, deject storage and cloud sync, often referred to every bit file sync and share (FSS). There are similarities amongst the three, just they are unlike processes.
File sync and share services allow users to create folders online where they tin store and access files stored on personal computers and servers. As the name implies, these services can automatically update files to their latest versions whether online or stored locally. They also make information technology easy for file sharing with colleagues or clients, and to work collaboratively. Cloud sync providers include Box, Dropbox, Google Drive and Microsoft OneDrive.
Some companies rely on file sync and share services to support their data equally well. While this arroyo might exist acceptable for a small amount of data, information technology is non appropriate for large data volumes or a company's critical data as these services tend to lack the types of direction and command features the deject fill-in offers. Likewise, given their user-oriented arroyo to data handling, data may become vulnerable if mishandled past sync and share participants.
Cloud fill-in vs. deject storage
Although they share similarities, they aren't the aforementioned thing. Cloud storage is a service model in which information is stored on remote systems. Data in cloud storage is available to users over a network, typically the internet. Benefits of cloud storage include global availability, ease of use and off-site security. Potential drawbacks range from performance bug depending on network connection to loss of complete control over the data to escalating costs over fourth dimension.
There are 3 main types of deject storage: public, individual and hybrid. Public cloud information is stored in the service provider'due south data heart. Customers pay based on several factors, including frequency and volume of data accessed. The superlative three public deject storage providers are Amazon, Google and Microsoft. Individual cloud storage is typically through in-house storage protected backside an organization'due south firewall. Private deject users often need more customization and control over their data. A hybrid model is a mix of public and private cloud storage.
As cloud backup is a service that sends an extra re-create of an organisation's information over a network to an off-site server, the typical user shouldn't need to access that data on a regular ground. Cloud storage, though, is for more regular utilise.
Deject storage itself should take backup. For example, an organization could back up data it has in AWS or Microsoft Azure with the provider'due south native fill-in or utilise a third-party tool.
Archiving is a adept use example for common cold cloud storage, but merely to a point. The infrequently accessed tier of deject storage provides a insufficiently cheaper price to store information that an organization must keep but doesn't need to regularly access. Yet, organizations should tread carefully hither, because costs add up as volumes rise and the toll to get data out is loftier.
Hybrid cloud backup
Hybrid cloud fill-in providers connect traditional backups to the cloud. This strategy is useful for organizations that produce a large volume of data and need quick restore admission. With i approach, a NAS appliance serves every bit a local backup target and syncs backup data to the cloud. When an organization needs a quick restore, the information is available in the on-site NAS. If an organization loses its primary site, the deject backup is still available, protecting against information loss. This method tin can also exist referred to as D2D2C backup. In another hybrid approach, an organization uses both the public and private deject for backup.
Information technology is difficult to go data consistency with hybrid cloud backup, especially if the information transfer takes a long time. Point-in-fourth dimension snapshots and continuous backups assistance, but costs ascent as backup frequency increases.
Comparatively, in a pure deject backup scenario, backups get directly to the service provider'due south cloud.
Cost
Third-party deject fill-in initially gained popularity with SMBs and home users because of its convenience. Today, cloud backup services take become more than sophisticated and can offering the same level of information protection, if not greater, equally in-house data fill-in.
The technology has an initial upfront cost to implement, but its lower monthly or yearly payment plans appeal to many smaller operations. Uppercase expenditures for additional hardware are not required and backups can be run dark. Nonetheless, the toll of keeping data in the deject for years does add upward. In addition, costs rise as the amount of data backed up to the cloud increases. A system of effective data grooming and archiving can assist go along costs down.
Ben Woo, managing manager of Neuralytix, explains how to evaluate cloud fill-in costs.
In terms of return on investment, information technology is important for an organisation to consider the long-term costs of backing up to the deject. A five-year projection is recommended to properly gauge future expenses and to make up one's mind whether the cloud volition help an organisation pause even afterward initial costs. Later these costs are offset, ROI on cloud-based backups can be adamant.
Pricing models vary by vendor, only it is important to wait out for hidden costs in cloud fill-in services. While well-nigh products for backing upwardly to the cloud are sold using a price-per-gigabyte-per-calendar month payment model, providers tin can too use a sliding calibration model, set usage minimums and add transaction costs.
Security
Security is an important element in the cloud backup procedure. The three master considerations are ofttimes referred to equally the security CIA: confidentiality, integrity and availability.
Most data volition move across the public internet on its way to the cloud, and then for confidentiality, many cloud backup providers encrypt information throughout the process: at the original location, during transit and at rest in the provider's information center. A user or the provider holds the encryption key. Nearly organizations prefer to hold their encryption keys, and providers should offer this option. Types of network encryption include Secure Sockets Layer and Transport Layer Security protocols.
For integrity, users must make up one's mind if data is the same when it is read dorsum or if it was corrupted. Object storage offers built-in integrity checks.
Availability takes the restoration process into account. It asks: Will data be bachelor in a timely fashion in a disaster recovery situation?
Access control is also of import. An organization tightens security by limiting access to cloud backups. Furthermore, write-once, read-but admission protects fill-in data from being overwritten, altered or deleted.
Vendor options
Approaches to online backup services vary, then an organisation should take a close look at SLAs, pricing plans and long-term costs before choosing a provider. Examples of cloud data backup vendor options include the following:
- Acronis offers Cyber Backup Cloud, a hybrid cloud backup-as-a-service production. Acronis Cyber Backup Cloud protects virtual, physical and deject environments, and includes a pay-as-y'all-go business model.
- Arcserve expanded its Unified Data Protection (UDP) offering with its buy of Zetta. The product includes Arcserve UDP Cloud Direct directly-to-cloud disaster recovery and backup. The deject protection is targeted at the midmarket.
- Asigrais a cloud backup pioneer. Its Deject Backup features embedded malware engines to prevent ransomware from getting into backups.
- Backblaze offers personal and business cloud backup, as well as cloud storage. Backblaze stores data on its open up source Storage Pods hardware platform and cloud-based Backblaze Vault file system. Fill-in data through Backblaze is accessible through a web browser on mobile devices and computers. Restores are downloaded over SSLs.
- Carbonite sells to consumers, SMBs and enterprises. The company's offerings support documents, email, music, photos and settings and are bachelor for Windows and Mac users. In March 2018, Carbonite caused rival Mozy from Dell EMC and incorporated its services into its offerings. In 2019, Carbonite bought cybersecurity vendor Webroot. Later in 2019, content management vendor OpenText acquired Carbonite.
- Druva cloud fill-in features three major offerings. The enterprise-level Druva inSync is targeted at endpoints and backs upwardly information across physical and public cloud storage, while Phoenix is a software agent used to back up and restore data sets in the cloud for distributed physical and virtual servers. In addition, in 2018, Druva acquired CloudRanger for AWS data protection.
- IDrive cloud fill-in is geared toward consumers and modest businesses and includes snapshots, a syncing service and hybrid data protection.
- Microsoft Azure Backup automatically sends backups to the Azure cloud. Azure Site Recovery automates replication to back up private Windows infrastructure.
- Unitrends allows customers to dorsum up indefinitely to its private cloud with Forever Deject. It offers several disaster recovery as a service (DRaaS) options for recovery.
- Veeam Software provides cloud backup through its Cloud Connect product. Service providers can partner with Veeam to create a backup and recovery target in the deject.
This was concluding updated in August 2020
Continue Reading About What is deject backup and how does information technology piece of work?
- Explore why deject fill-in is a expert choice for small businesses
- Cloud backup tin can help remote workforce
- Be careful with cost of deject backup as information volume grows
- Handbook details cloud backup services and ransomware protection features
- How cloud storage providers stack upwards for backups
torreshavocapiente.blogspot.com
Source: https://www.techtarget.com/searchdatabackup/definition/cloud-backup
0 Response to "If I Cancel During Middle of Backing Up Then When I Back Up Again Do Data Gets Duplicated"
Enregistrer un commentaire